 +86-13928815851
+86-13928815851
Leave Your Message
-
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER -
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER -
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER



Ultra-Thin Batteries have emerged as a transformative innovation in the realm of modern technology, driven by the ever-increasing demand for compact and efficient power sources. As consumer electronics continue to shrink in size while demands for performance escalate, ultra-thin batteries play a critical role in powering devices ranging from smartwatches to advanced medical equipment. Industry reports indicate that the global market for thin film batteries is expected to reach $1.12 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 21.6%. This surge is primarily fueled by advancements in materials science and engineering, leading to batteries that not only match the electrical density of traditional counterparts but also offer significant reductions in weight and volume.
The functionality of Ultra-Thin Batteries hinges on their unique construction, which often incorporates lithium-ion technology with innovative layering techniques to minimize thickness while maximizing energy efficiency. This enables them to be seamlessly integrated into various applications, enhancing the design capabilities of electronics manufacturers. Furthermore, with the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and wearable technology, the need for such compact power sources is more pronounced than ever. As devices become increasingly interconnected and feature-rich, the reliance on ultra-thin batteries will continue to grow, ushering in new possibilities for innovation across multiple sectors, including healthcare, consumer electronics, and automotive technology.

Ultra-thin batteries are revolutionary power sources designed to meet the growing demands of modern technology. These batteries are characterized by their remarkably slim profiles, often measuring just a fraction of a millimeter in thickness. This unique feature enables them to be seamlessly integrated into compact devices such as smartphones, wearables, and even flexible electronics. The construction of ultra-thin batteries typically employs advanced materials and innovative techniques, allowing for high energy density without compromising on performance or safety.
In addition to their slim design, ultra-thin batteries boast several key features that make them ideal for contemporary applications. They are lighter than traditional battery designs, contributing to the overall reduction in device weight. Furthermore, they can maintain high efficiency and stability over prolonged use, ensuring that modern gadgets remain powered through demanding tasks. Their flexible nature allows manufacturers to create diverse product shapes and sizes, opening new possibilities for innovative technology in everyday items and specialized applications.
As technology continues to evolve, the role of ultra-thin batteries will undoubtedly expand, driving the development of even more advanced and versatile devices.
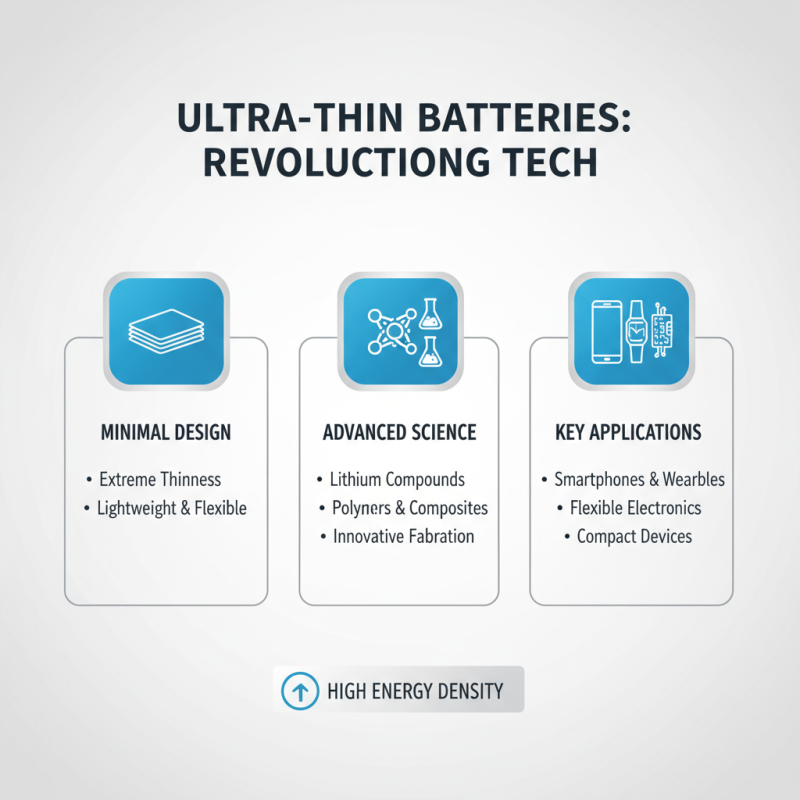
Ultra-thin batteries are revolutionizing the landscape of modern technology, characterized by their minimal thickness and lightweight design. The science behind these batteries primarily involves advanced materials and innovative fabrication techniques. Common materials used in ultra-thin batteries include lithium compounds, polymers, and composite materials, which contribute to their efficiency and flexibility. These materials enable the batteries to maintain a high energy density while dramatically reducing their volume and weight, making them ideal for applications in smartphones, wearables, and flexible electronics.
To achieve the ultra-thin form factor, manufacturers utilize thin-film technology and advanced manufacturing processes such as roll-to-roll production. Thin-film batteries are constructed by layering materials in a very thin format, allowing for rapid energy storage and discharge cycles. This not only enhances the performance of electronic devices but also allows for integration into various surfaces and shapes, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in design. The focus on sustainability and the development of eco-friendly materials is also pivotal in the ongoing evolution of ultra-thin battery technology, ensuring that they meet the growing demands for clean energy solutions in the tech industry.
Ultra-thin batteries are revolutionizing the consumer electronics and wearables market by providing lightweight, flexible power solutions without compromising performance. These advanced energy storage devices typically measure just a few millimeters thick, making them ideal for integration into sleek, modern devices such as smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches. Their thin profile allows manufacturers to create designs that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also more ergonomic, enhancing user experience while maintaining functionality.
The applications of ultra-thin batteries extend beyond traditional consumer electronics to wearable technology, which is rapidly growing in popularity. Fitness trackers, smart clothing, and health monitoring devices all benefit from these compact power sources. As wearables require continual energy to operate sensors and connectivity features, ultra-thin batteries offer the perfect combination of efficiency and longevity, ensuring that these devices can be worn comfortably throughout the day without the hassle of frequent recharging. This synergy between ultra-thin batteries and wearable technology is paving the way for innovative health solutions and smarter lifestyle choices.
| Application | Battery Type | Thickness (mm) | Capacity (mAh) | Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smartphones | Lithium Polymer | 0.55 | 1500 | 3.7 |
| Wearable Fitness Trackers | Li-Ion Film | 0.3 | 100 | 3.7 |
| Smart Watches | Thin Film Battery | 0.5 | 250 | 3.7 |
| Bluetooth Earbuds | Flexible Lithium Battery | 0.4 | 60 | 3.7 |
| Medical Wearables | Solid-State Battery | 0.2 | 300 | 3.0 |
Ultra-thin batteries have emerged as a groundbreaking solution in the realm of modern technology, offering compact and lightweight energy sources for an array of applications. Their energy density—the amount of energy that can be stored per unit volume or weight—plays a crucial role in determining their effectiveness compared to traditional battery technologies. Generally, ultra-thin batteries can deliver energy densities quite similar to those of conventional batteries, but with the added advantages of a slimmer profile and flexibility. This makes them particularly suitable for devices that require minimal size without compromising performance, such as wearable electronics and advanced portable gadgets.
Moreover, the efficiency of ultra-thin batteries often surpasses that of their thicker counterparts. Enhanced efficiency is achieved through improved materials and innovative designs that optimize charge and discharge cycles. This not only extends the lifespan of the batteries but also ensures that devices can operate longer on a single charge, which is vital for user satisfaction. When employed in electric vehicles or energy-harvesting applications, ultra-thin batteries can contribute to a more sustainable energy ecosystem, further solidifying their role in the future of technology. As research and development continue to advance in this field, we can expect these batteries to become even more efficient and energy-dense, driving innovation across numerous sectors.
The development of ultra-thin batteries is at the forefront of technological innovation, with significant implications for the future of portable and wearable devices. These batteries, which typically measure just a few millimeters in thickness, enable manufacturers to design sleeker, lighter products without compromising on battery life. This is particularly critical in applications like smartwatches, augmented reality glasses, and flexible electronics, where space is limited. As research advances, newer materials like graphene and solid-state components are being explored to enhance energy density and safety, paving the way for more powerful and efficient energy storage solutions.
However, the path to widespread adoption of ultra-thin batteries is not without challenges. One of the primary obstacles is ensuring durability and performance under various conditions. The thin structure can compromise the battery's resilience to temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress, which could lead to decreased lifespan and reliability. Additionally, the manufacturing processes for these batteries may require significant investment in new technologies and infrastructure, posing barriers for mass production. Addressing these issues through innovative engineering and material science will be crucial for successfully integrating ultra-thin batteries into everyday technology, making them a reliable choice for consumers worldwide.






